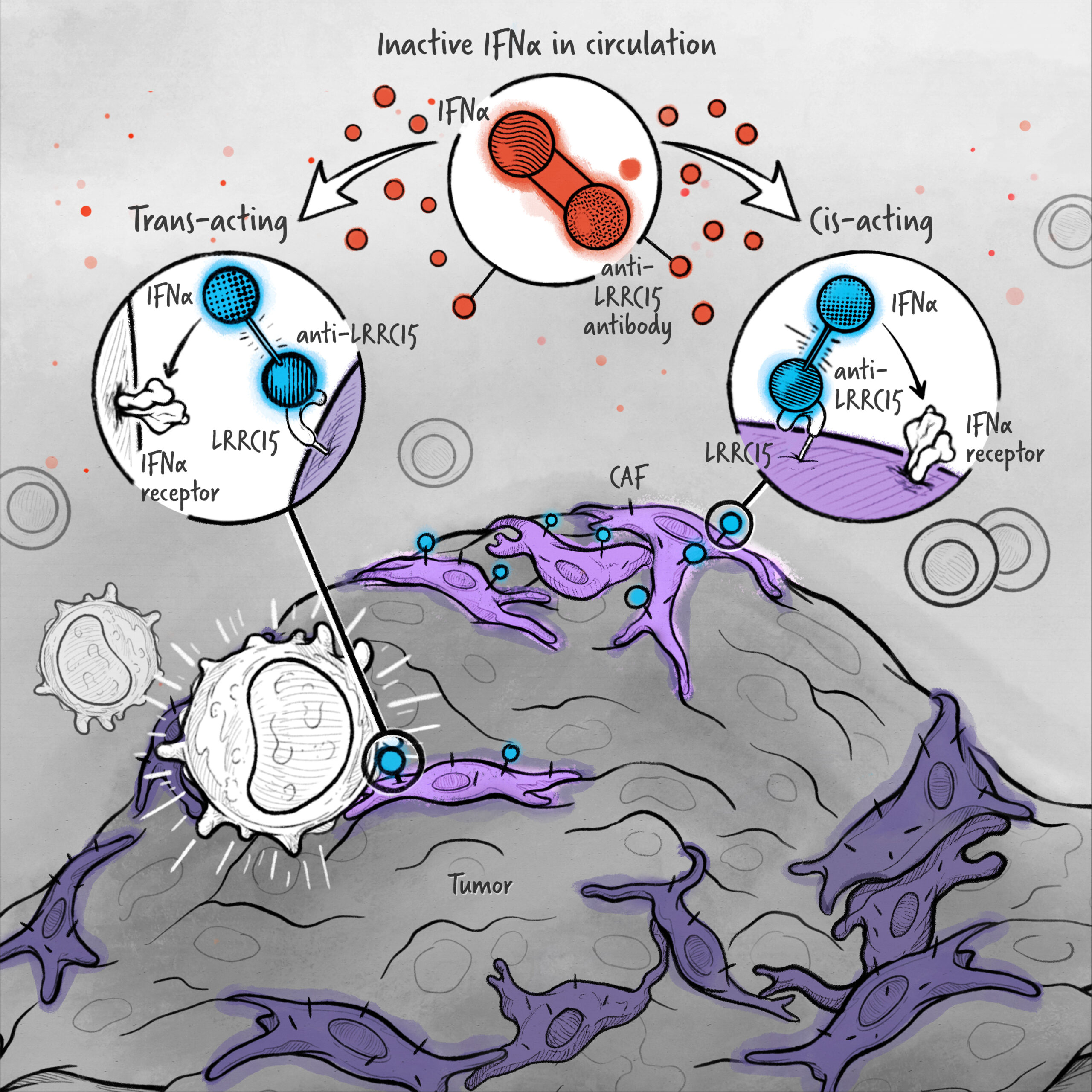
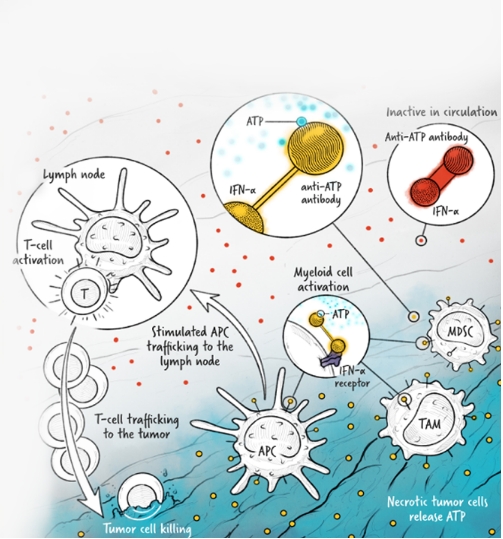
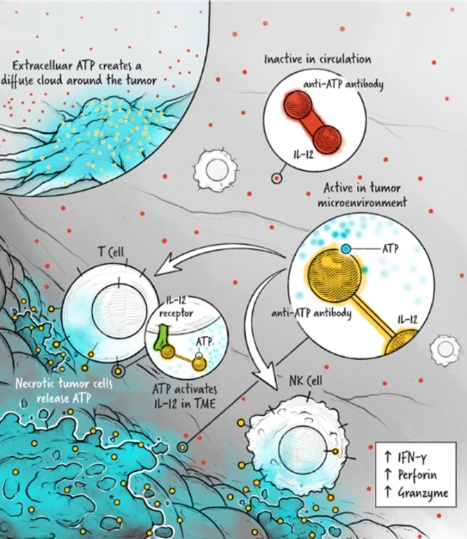
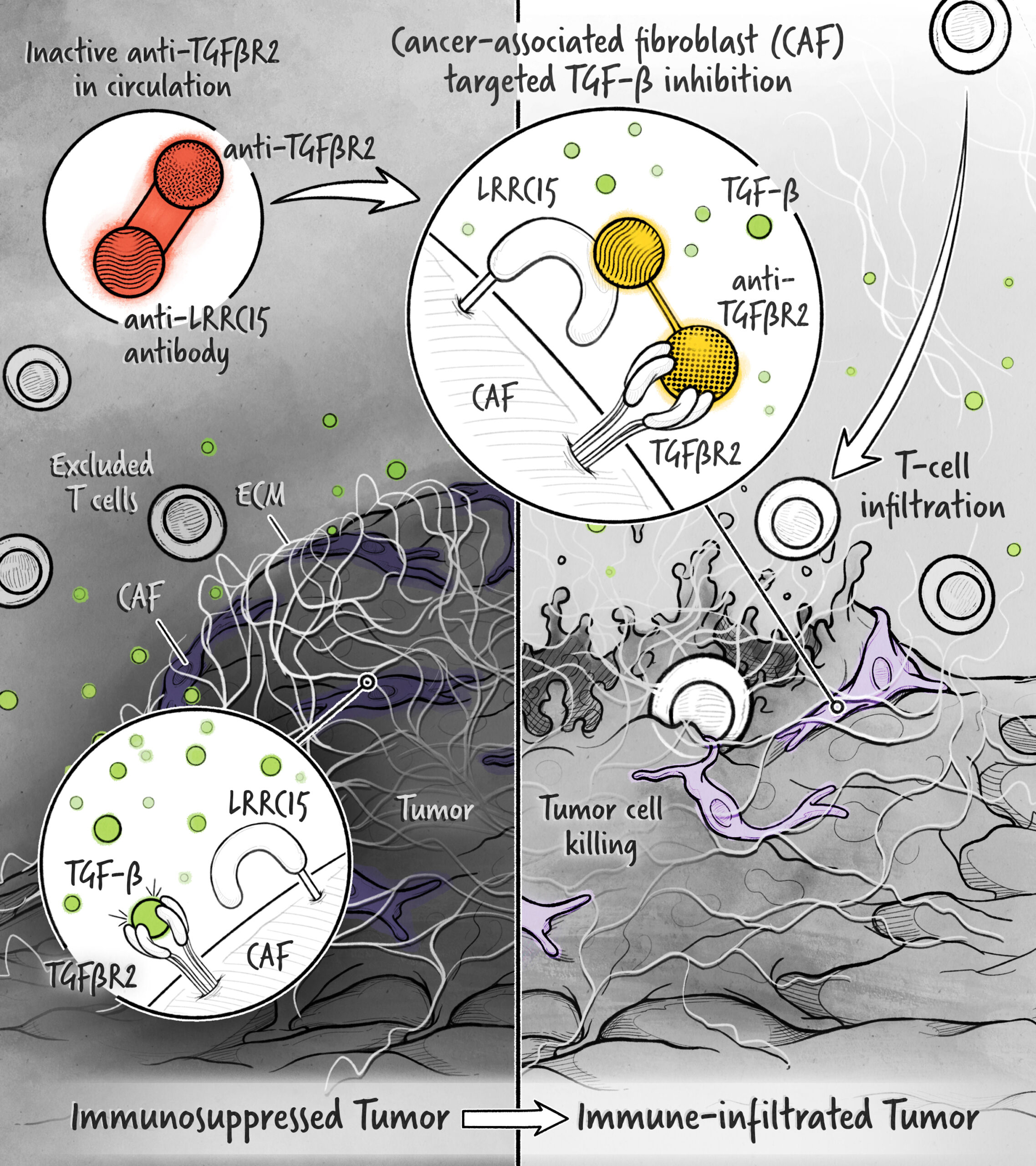
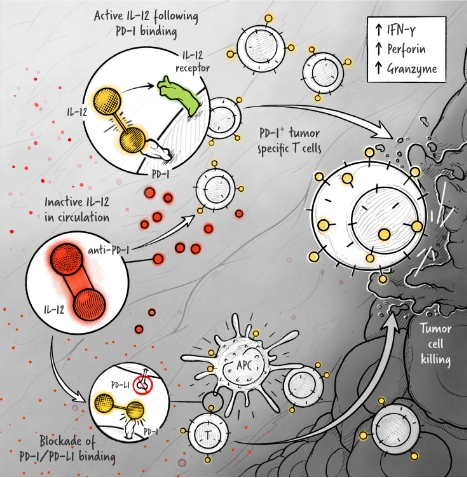
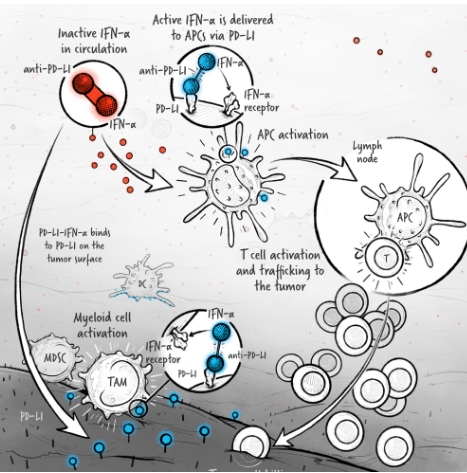
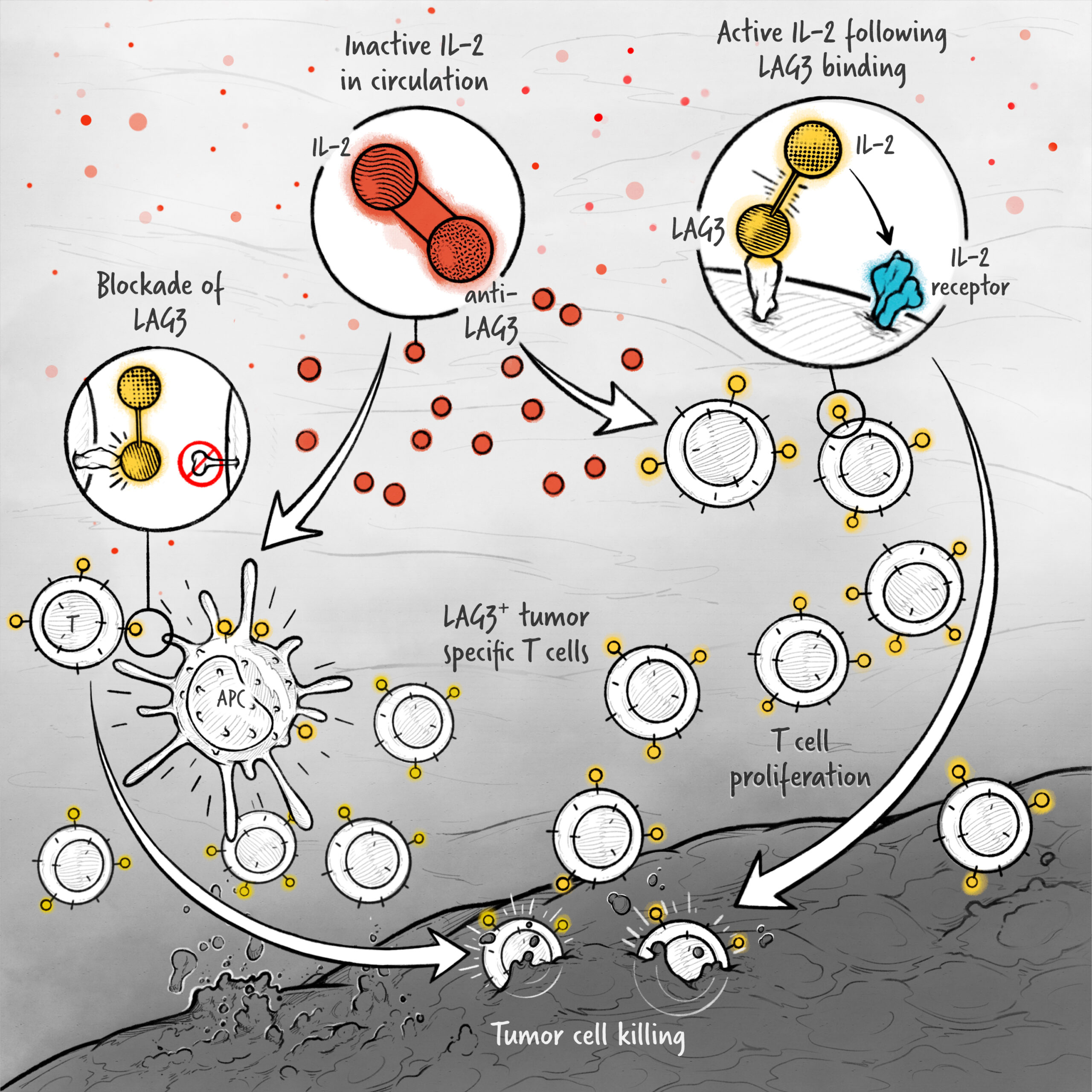
The cytokines IL-2, IFN-α, and IL-12 are potent activators of the immune system whose application in the treatment of cancer has been limited by toxicity and lack of efficacy. We are developing cytokine drugs that are only active following binding of the construct to a specified target. Our therapeutics have the potential to be more effective than systemically active native or attenuated cytokines.
Additionally, a growing body of data has implicated the TGF-β pathway as a key contributor to the immunosuppressed state of the tumor microenvironment.
With our technology, we are developing highly targeted inhibitors that allow for the therapeutic modulation of this pleiotropic and complex pathway.